A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective.
Price floor surplus or shortage.
A demand curve on a demand supply graph depicts the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity of the product demanded at that price.
The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the equilibrium values of economic variables will not change often described as the.
The department of agriculture purchases surplus crops for.
So government has to intervene and buy the surplus inventories.
When price floor is continued for a long time supply surplus is generated in a huge amount.
A price floor is an established lower boundary on the price of a commodity in the market.
We call this equilibrium which means balance in this case the equilibrium occurs at a price of 1 40 per gallon and at a quantity of 600 gallons.
Governments usually set up a price floor in order to ensure that the market price of a commodity does not fall below a level that would threaten the financial existence of producers of the commodity.
We call a surplus caused by the minimum wage unemployment.
Demand curves are highly valuable in measuring consumer surplus in terms of the market as a whole.
An example of a binding price floor established by law but carried out through government purchases is agricultural price supports.
Unfortunately it like any price floor creates a surplus.
When government laws regulate prices instead of letting market forces determine prices it is known as price control.
In this case it is a surplus of workers suppliers of labor more of whom are willing to work in minimum wage jobs than there are employers demanders willing to hire at that wage.
Due to the law of diminishing marginal utility the demand curve is downward sloping.
In case of producer surplus producers would have reduced the price to increase consumers demands and clear off the stock.
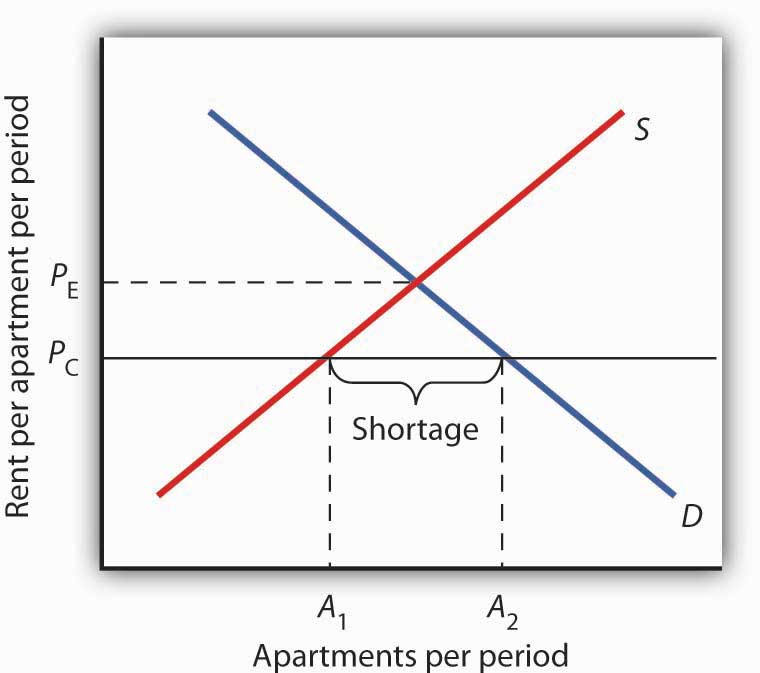
A price ceiling below the market price creates a shortage causing consumers to compete vigorously for the limited supply limited because the quantity supplied declines with price.
A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service.
Likewise since supply is proportional to price a price floor creates excess supply if the legal price exceeds the market price.
When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price quantity demanded will exceed quantity supplied and excess demand or shortages will result.
Price floors prevent a price from falling below a certain level.
When the surplus is eliminated the quantity supplied just equals the quantity demanded that is the amount that producers want to sell exactly equals the amount that consumers want to buy.
When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price quantity supplied will exceed quantity demanded and excess supply or surpluses will result.